When it comes to printing output in programming, printf is one of the most commonly used functions, especially in languages like C, Shell scripting, and Java. Understanding its functionality, capabilities, and alternatives can significantly enhance your coding experience.
Contents
- 1 What is printf?
- 2 Common Usage and Examples in Shell Scripts
- 3 Using %q in Shell printf
- 4 Format Specifiers in Shell printf
- 5 Alternatives to printf in Shell Scripts
- 6 When to Use printf in Shell Scripts
- 7 Scenario-Based Interview Questions and Answers
- 7.1 1. How would you use “ to escape special characters in a user input string?
- 7.2 2. How can you format a floating-point number to show exactly three decimal places?
- 7.3 3. How can you create a table with aligned columns using “?
- 7.4 4. What happens if a format specifier does not match the argument type?
- 7.5 5. How do you print a literal ** character using **?
What is printf?
The printf function stands for “print formatted” and is used to print formatted output to the console. It provides a powerful way to display text, numbers, and other data types in a customized format. Primarily, it is a standard library function in C but is also available in shell scripting for Unix/Linux environments.
Syntax in Shell Scripts:
printf FORMAT [ARGUMENT]...Unlike echo, which simply prints text, printf provides advanced formatting capabilities.
Common Usage and Examples in Shell Scripts
Basic Printing
The simplest use of printf is to display static text:
printf "Hello, World!\n"Note: Unlike echo, you must explicitly include \n for a new line.
Printing Variables
You can use format specifiers to print variable values:
name="Alice"
age=30
printf "Name: %s\nAge: %d\n" "$name" "$age"Formatting Numbers
printf allows precise control over numerical output:
pi=3.14159
printf "Value of pi: %.2f\n" "$pi" # Limits to 2 decimal placesCreating Aligned Tables
You can use width specifiers to align output:
printf "| %-10s | %5s |\n" "Name" "Score"
printf "| %-10s | %5d |\n" "Alice" 90
printf "| %-10s | %5d |\n" "Bob" 85Output:
| Name | Score |
| Alice | 90 |
| Bob | 85 |Using %q in Shell printf
The %q specifier in printf escapes special characters in a string, making it useful for safe and predictable output, especially when dealing with untrusted input or special characters.
Example:
input="Hello, $USER!"
printf "%q\n" "$input"Output:
Hello,\ \$USER!This is particularly helpful in scripts where inputs might include spaces, quotes, or other characters requiring escaping.
Combining %q with Other Specifiers:
user_input="Alice & Bob"
printf "Escaped input: %q\n" "$user_input"Output:
Escaped input: Alice\ \&\ BobFormat Specifiers in Shell printf
Here are some common placeholders used in shell scripting with printf:
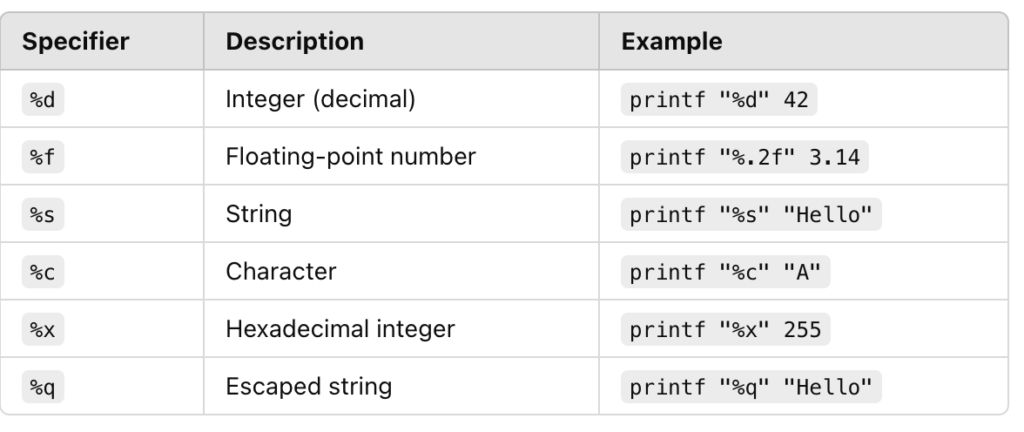
Differences Between printf and echo

Alternatives to printf in Shell Scripts
While printf is versatile, there are alternatives for simpler tasks:
1. “
The echo command is simpler and often sufficient for basic output.
echo "Hello, World!"2. “** for Advanced Formatting**
awk can be used for complex text processing and formatting.
echo "Alice 90\nBob 85" | awk '{ printf "| %-10s | %5d |\n", $1, $2 }'3. “** for Static Text**
For displaying static text files or strings, cat is an option:
cat <<EOF
Hello, World!
EOFWhen to Use printf in Shell Scripts
- Precision Formatting: When output requires specific formatting, such as aligned tables or controlled decimal places.
- Dynamic Data: To print variables or user inputs in a structured way.
- Escaping Input: Use
%qfor handling special characters safely. - Script Portability: Ensures consistent behavior across different Unix/Linux environments.
Scenario-Based Interview Questions and Answers
1. How would you use “ to escape special characters in a user input string?
Answer: Use the %q format specifier to ensure that special characters are escaped.
input="Hello, $USER!"
printf "%q\n" "$input"This will output: Hello,\ \$USER!
2. How can you format a floating-point number to show exactly three decimal places?
Answer: Use %.3f in the format specifier.
pi=3.14159
printf "%.3f\n" "$pi"This will output: 3.142
3. How can you create a table with aligned columns using “?
Answer: Use width specifiers to align the text.
printf "| %-10s | %5s |\n" "Name" "Score"
printf "| %-10s | %5d |\n" "Alice" 90
printf "| %-10s | %5d |\n" "Bob" 854. What happens if a format specifier does not match the argument type?
Answer: The output may be unpredictable, as printf does not perform type checking. For example:
printf "%d\n" "string"This could cause an error or display an unintended result.
5. How do you print a literal ** character using **?
Answer: Use %% in the format string.
printf "Progress: 50%%\n"This will output: Progress: 50%
The printf command is a powerful tool in shell scripting, offering advanced formatting capabilities beyond what echo can provide. Its versatility makes it a go-to choice for scripts that require precision and control over the output format. While simpler alternatives exist, understanding and leveraging printf ensures your shell scripts are robust and professional.
Experiment with printf in your shell scripts and discover how it can streamline and enhance your output!


